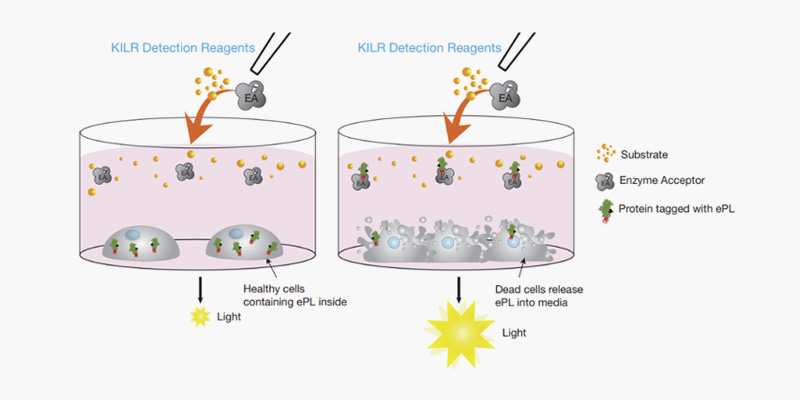
Fig1. KILR Detection: , the well on the left
contains intact target cells that are alive in the presence of immune effector
cells. When detection reagents are added to the well, we cannot detect
chemiluminescence as the reporter protein does not leak out through an intact
cell membrane into the media. In contrast, in the well on the right, after
addition of antigen-specific antibody, the target cells are killed by the KILR
CD16 Effector Cells, releasing the reporter protein into the media. Addition of
the detection reagents leads to the recognition of the reporter protein and
generation of a chemiluminescent signal that is proportional to the number of
dead cells. Death of any other cell type, including the KILR CD16 Effector
Cells present within the co-culture will not affect the assay output, giving
the KILR cytotoxicity assay an unparalleled specificity to detect target cell
death within a co-culture system.
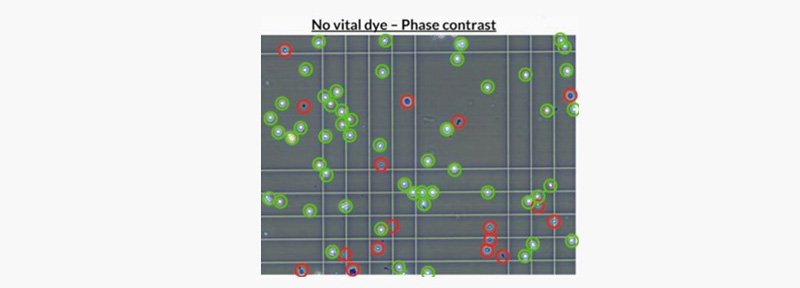
Fig2. Representative image of KILR CD16 Effector Cells
under phase-contrast microscope. Viable KILR CD16 Effector Cells (to be
counted) in green, Cells that should NOT be counted as live cells (Not viable
or active as effector cells) in red.

Fig3. Typical results for anti-CD20 antibody-mediated
ADCCKILR Raji cells stably expressing the ePL-labeled housekeeping protein were
washed and resuspended in CP39 medium, opsonized with a titration of anti-CD20
antibody, then incubated with KILR CD16 Effector cells. An E:T ratio of 10:1 or
an equivalent volume of vehicle E:T ratio of 0:1 was used. After 4 hours, KILR
Detection Reagent was added to the medium and incubated for one hour prior to
detection of luminescence signal on a luminescence plate reader (Envision, PE).
 Eurofins Discovery
Eurofins Discovery


 Eurofins Discovery
Eurofins Discovery