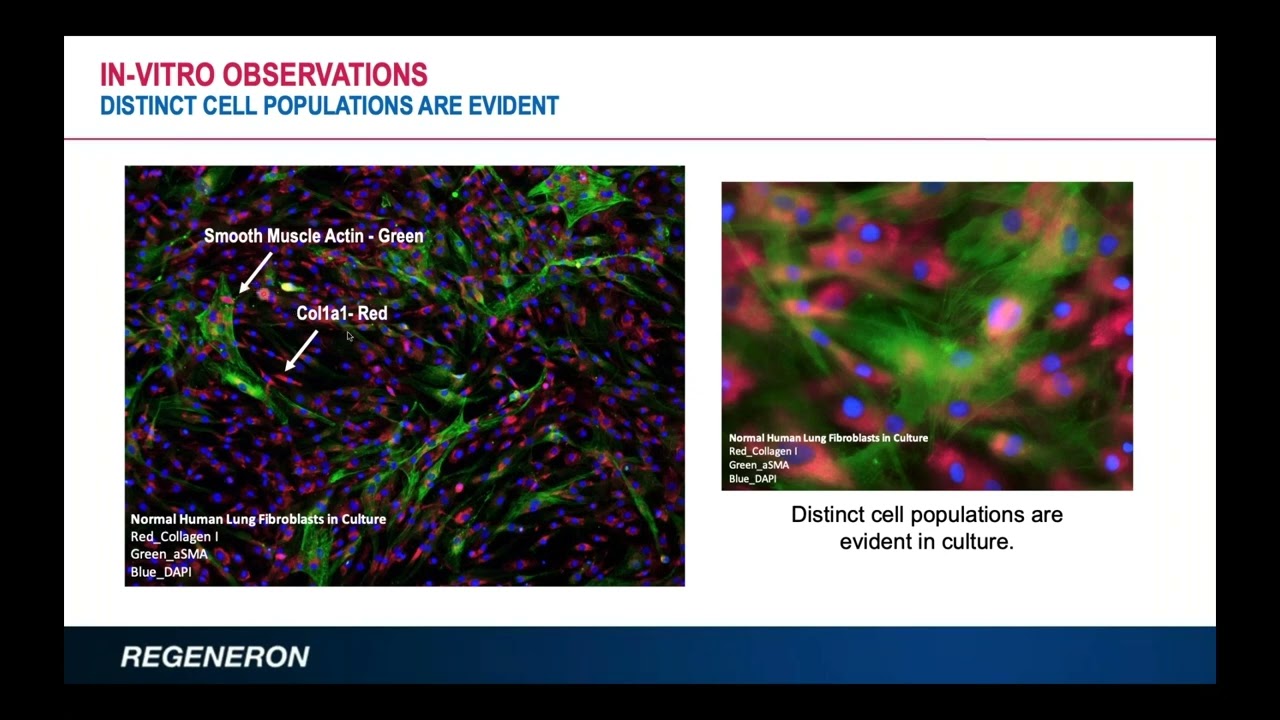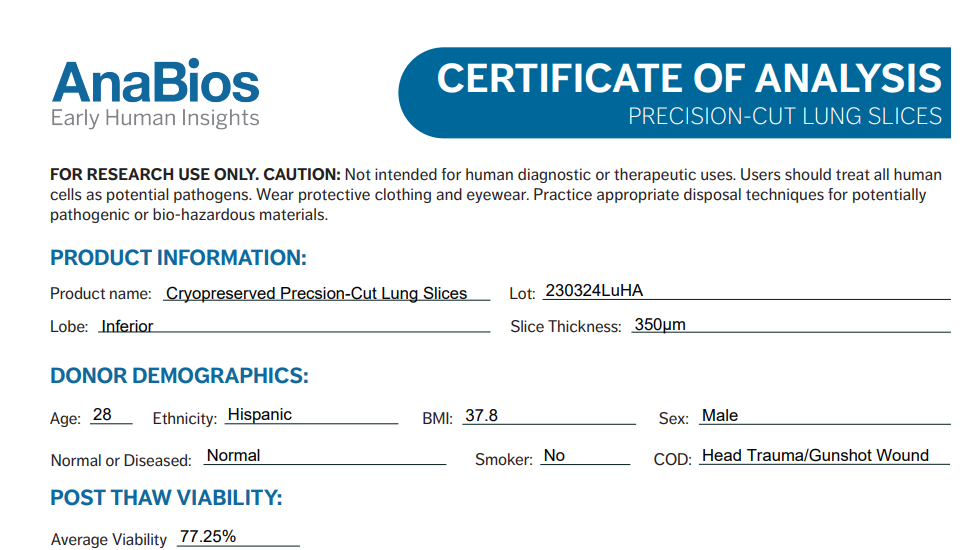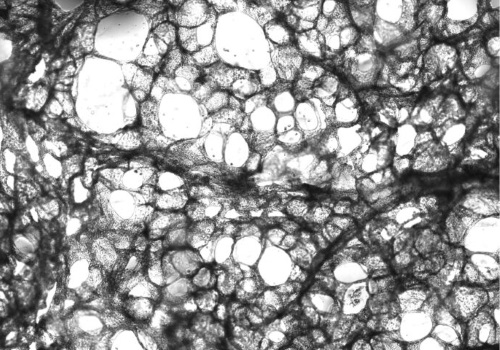
 Anabios
Anabios
Precision-Cut Lung Slices (hPCLS)
AnaBios에서는 약물 개발 및 호흡기 연구에 활용할 수 있는 인간 폐 조직에서 정밀하게 절단된 Precision-Cut Lung Slices (hPCLS)를 제공합니다.
제품 소개
AnaBios는 기증에 동의한 성인들로부터 윤리적으로 기증 받은 Primary Tissue를 제공합니다. AnaBios의 Precision-Cut Lung Slices (hPCLS)는 인간 폐 조직의 복잡한 구조와 세포 구성을 그대로 유지하여 ex vivo 환경에서 폐의 생리적 특성을 재현할 수 있도록 합니다. 정상 조직과 질환 조직(예: COPD, Fibrosis)을 비롯하여 성별, 나이, 인종, BMI를 비롯한 인구통계학적 정보가 같이 제공되고 있어, 약물 효능 평가, 독성 연구 및 질병 모델링에 활용이 가능합니다.
- 폐 조직의 복잡한 구조를 유지
- 높은 RNA Integrity (RIN) Score으로 검증된 고품질
- 최적화된 보존 기술
- 질병 모델링이 아닌 질병 샘플을 이용, 높은 생물학적 연관성
데이터 자료
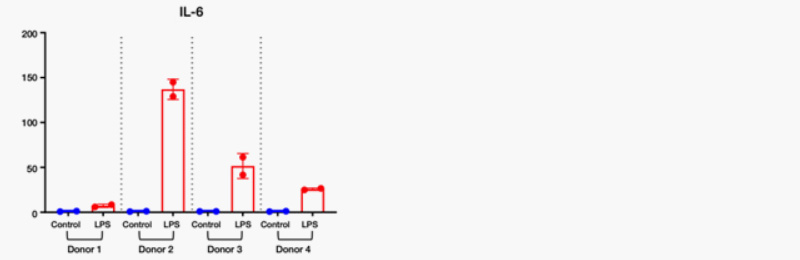
Fig1. Human PCLS Samples Show Inflammatory Responses
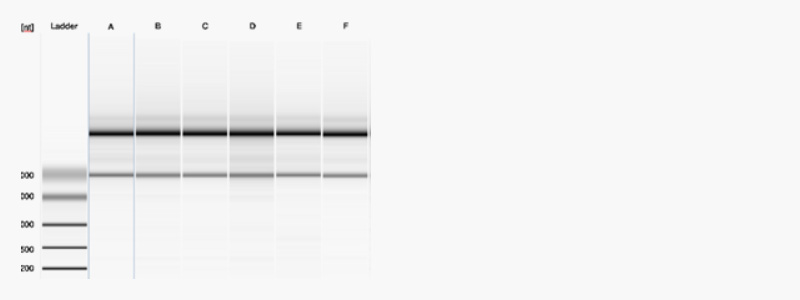
Fig2. Northern Blot of Precision-Cut Lung Slices from Six Different Donors
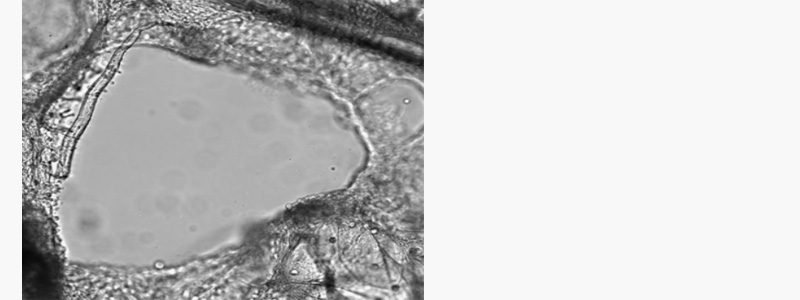
Fig3. Thawed PCLS Demonstrates High Viability
추천대상
신뢰성 있는 폐 질환 모델링
폐 질환 연구소
AnaBios의 hPCLS는 COPD 및 섬유화 모델링 연구에서 실험 결과의 신뢰성이 높아져 연구 효율을 크게 향상시킬 수 있습니다.
해동 후 높은 생존율과 기능성
임상 진입 전의 바이오텍
동결 보존 샘플로도 좋은 성능을 보여줍니다. 해동 후 높은 생존율과 기능성을 유지해 데이터 변동성을 줄일 수 있습니다.
원하는 인구 집단에서 기증된 샘플
중개연구가 필요한 제약사
원하는 인구 집단에서 기증된 샘플에서 데이터를 얻을 수 있어 유용합니다. 적절한 정보가 제공되어 연구에 편리합니다.
Publication (2)
The pivotal role of myofibroblast contractility in the pathophysiology of fibrosis is widely recognized, yet HTS approaches are not available to quantify this critically important function in drug discovery. We developed, validated, and scaled-up a HTS platform that quantifies contractile function of primary human lung myofibroblasts upon treatment with pro-fibrotic TGF-β1. With the fully automated assay we screened a library of 40,000 novel small molecules in under 80 h of total assay run-time. We identified 42 hit compounds that inhibited the TGF-β1-induced contractile phenotype of myofibroblasts, and enriched for 19 that specifically target myofibroblasts but not phenotypically related smooth muscle cells. Selected hits were validated in an ex vivo lung tissue models for their inhibitory effects on fibrotic gene upregulation by TGF-β1. Our results demonstrate that integrating a functional contraction test into the drug screening process is key to identify compounds with targeted and diverse activity as potential anti-fibrotic agents.
View publication
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic, progressive lung disease characterized by scarring and tissue remodelling. Current treatments have limited efficacy and significant side effects. To address these limitations, we developed AD-214, an anti-CXCR4-Fc-fusion protein comprised of an anti-CXCR4 i-body (AD-114) tethered at its C terminus to constant domains 2 and 3 of the Fc region of a mutated human IgG1 lacking effector function. AD-214 binds with high affinity and specificity to CXCR4, modulates intracellular signaling and inhibits key fibrotic pathways. Using fibrosis models, we demonstrate that AD-214 treatment significantly reduces collagen deposition and lung remodelling and has a unique mode of action. In Phase 1 clinical trials intravenous (IV) infusion of AD-214 led to high and sustained CXCR4 receptor occupancy (RO); however, whether RO and efficacy are causally linked remained to be determined. Herein, we demonstrate that CXCR4 RO by AD-214 inhibits primary human leukocyte migration, a model fibrotic process, and that migration inhibition is achievable at concentrations of AD-214 present in the serum of healthy human volunteers administered AD-214. Taken together, these data provide proof of concept for AD-214 as a novel treatment strategy for IPF, and suggest that clinically feasible dosing regimens may be efficacious.
View publication
문의하기
Precision-Cut Lung Slices (hPCLS)